Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
All content on Eyewiki is protected by copyright law and the Terms of Service. This content may not be reproduced, copied, or put into any artificial intelligence program, including large language and generative AI models, without permission from the Academy.
Overview
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are small molecules that act on tyrosine kinase receptors to modulate downstream signaling pathways. These compounds have an emerging role in the management of retinal disease using VEGF inhibition, and various forms of these compounds and routes of application are currently under investigation. TKIs are expected to play an important role in transforming current treatment paradigms and reducing treatment burden for patients with certain retinal conditions.
Mechanism
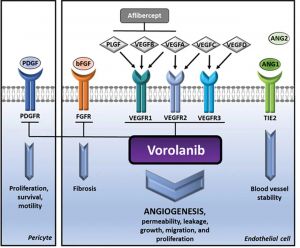
The VEGF receptor (VEGFR) is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK). Upon ligand binding, RTK extracellular components dimerize and assume active conformation, leading to activation of the intracellular RTK domain. Induced autophosphorylation of intracellular domain tyrosines recruits and activates downstream signaling molecules Shc, Grb2, Nck, and phospholipase C-γ1 to activate phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3 K)/Akt, focal adhesion kinases (FAK), and MAPK pathways [Dong et al]. These pathways mediate cell adhesion, migration, intracellular trafficking, metabolism and aging, proliferation, growth, and survival processes [1] [2] [3]. Anti-VEGF medications exert their effect by preventing VEGF from binding to extracellular receptors and preventing the subsequent cascade of downstream effects. As small molecules, TKIs are able to diffuse into cells and inhibit RTKs by binding to their intracellular domains. A benefit of this approach is the targeting of a broader range of VEGFR isoforms along with inhibiting other RTKs such as platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR), and fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR), which have been shown to have roles in retinal angiogenesis [4].
Clinical Use
TKIs are not currently FDA-approved and remain in clinical trials.
How these medications will fit into future treatment paradigms is uncertain. The majority of trials have focused on patients with nAMD (either previously treated or treatment naive) or DME, but there has also been interest in treating diabetic retinopathy without DME.[7] It is hypothesized that TKIs may be used in conjunction with anti-VEGF to increase treatment durability, or as an alternative standalone treatment in the future. TKIs act on a different (intracellular) domain of VEGFRs compared to traditional anti-VEGF therapies (extracellular), potentially allowing for a complementary effect on decreasing receptor activity.
The 3 most extensively studied TKI agents are vorolanib, axitinib, and lenvatinib, but additional novel therapeutics remain under development. These medications are delivered using various routes, and the duration of effect is extended in some cases using proprietary sustained-release technologies.
Ongoing Clinical Trials
| Treatment | Manufacturer | Phase | Route | Additional Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duravyu (formerly EYP-1901 ) | Vorolanib | EyePoint Pharmaceuticals | Phase 3 | Intravitreal | Sustained release. Investigated nAMD in DAVIO 2 phase 2 trial, and DME in PAVIA phase 2 trial. |
| Axpaxli (formerly OTX-TKI) | Axitinib | Ocular Therapeutix | Phase 3 | Intravitreal | Sustained release over 9-12 months. HELIOS phase 1b trial treated NPDR without DME. SOL is a phase 3 trial treating nAMD. |
| AIV007 | Lenvatinib | AiViva BioPharma | Phase 1 | Periocular | Sustained release using gel suspension. Trial patients had nAMD or DME and previously responded to anti-VEGF.[8] |
| AXT107 | Gersizangitide (20-amino acid peptide) | AsclepiX Therapeutics, Inc. | Phase 1/2a | Suprachoroidal | Patients with nAMD enrolled in DISCOVER trial.[9] |
| D-4517.2 | Dendranib (class of TKI) | Ashvattha Therapeutics | Phase 2 | Subcutaneous or Oral | Patients with nAMD and DME enrolled in phase 2 TEJAS trial.[10] |
| GB-102 | Sunitinib | CalciMedica | Phase 2 | Intravitreal | Treated patients with nAMD in ALTISSIMO phase IIb trial. Migration of particles into AC with initial formulation, decreased with changes to formulation.[11][12] |
| CLS-AX | Axitinib | Clearside Biomedical | Phase 2b | Suprachoroidal | Insoluble suspension formulation to extend durability. Compared to intravitreal aflibercept for nAMD in ODYSSEY phase 2b trial. [13] |
| PAN-90806 | --- | Zhaoke Ophthalmology & PanOptica | Phase 1/2 | Topical | Administered as eye drops. Trialed in treatment naive nAMD patients. Initial formulation caused punctate keratopathy, but this improved with subsequent formulation.[14] |
References
- ↑ Fruman DA, Chiu H, Hopkins BD, Bagrodia S, Cantley LC, Abraham RT. The PI3K Pathway in Human Disease. Cell. 2017;170(4):605-635. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.029
- ↑ Tan X, Yan Y, Song B, Zhu S, Mei Q, Wu K. Focal adhesion kinase: from biological functions to therapeutic strategies. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2023;12(1):83. Published 2023 Sep 25. doi:10.1186/s40164-023-00446-7
- ↑ Braicu C, Buse M, Busuioc C, et al. A Comprehensive Review on MAPK: A Promising Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11(10):1618. Published 2019 Oct 22. doi:10.3390/cancers11101618
- ↑ Vishwakarma S, Kaur I. Molecular mediators and regulators of retinal angiogenesis. Semin Ophthalmol. 2023;38:2:124-133
- ↑ https://investors.eyepointpharma.com/static-files/502d269d-0d9c-40a7-a02f-4176a08f16ae
- ↑ Hershberger, V. The DAVIO2 trial: a phase 2, multicenter study of a single injection of EYP-1901 (vorolanib in the durasert E technology) vs aflibercept for previously treated wet age-related macular degeneration. Presented at: Hawaiian Eye and Retina; January 13-19, 2024; Wailea, HI.
- ↑ Study of EYP-1901 in patients with nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR). ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT05383209.
- ↑ Hannah Hershoff; Darlene Deecher; Jennifer Wang; Diane DS Tang-Liu. Periocular injection of AIV007 in the Treatment of Macular Edema due to Neovascular Age-related Macular Degeneration (nAMD) or Diabetic Macular Edema (DME): Preliminary Results of the Phase 1 Clinical Trial. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science June 2024, Vol.65, 237. https://iovs.arvojournals.org/article.aspx?articleid=2796352
- ↑ AsclepiX Therapeutics Completes Enrollment in DISCOVER Trial for Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration (nAMD). AsclepiX Therapeutics.https://asclepix.com/asclepix-therapeutics-completes-enrollment-in-discover-trial-for-neovascular-age-related-macular-degeneration-namd/
- ↑ Ashvattha Therapeutics. Ashvattha Therapeutics announces first patient dosed via subcutaneous administration of anti-angiogenic therapeutic D-4517.2 for wet AMD and DME in phase 2 chronic dosing study. News release. November 1, 2023. https://avttx.com/ashvattha-therapeutics-announces-first-patient-dosed-via-subcutaneous-administration-of-anti-angiogenic-therapeutic-d-4517-2-for-wet-amd-and-dme-in-phase-2-chronic-dosing-study/. Accessed June 14, 2025.
- ↑ Graybug Vision. A Phase 2b Multicenter Dose-Ranging Study Evaluating the Safety and Efficacy of Sunitinib Malate Depot Formulation (GB-102) Compared to Aflibercept in Subjects With Neovascular (Wet) Age-Related Macular Degeneration (ALTISSIMO Study). https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03953079 (2022).
- ↑ Hussain, R. M., Shaukat, B. A., Ciulla, L. M., Berrocal, A. M. & Sridhar, J. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Antagonists: Promising Players in the Treatment of Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 15, 2653–2665 (2021).
- ↑ Clearside Biomedical Announces Positive Topline Results from ODYSSEY Phase 2b Trial of Suprachoroidal CLS-AX in Wet AMD Achieving All Primary and Secondary Outcomes. Clearside Biomedical News Release. Published October 9, 2024. Accessed June 14, 2026. https://ir.clearsidebio.com/news-releases/news-release-details/clearside-biomedical-announces-positive-topline-results-odyssey
- ↑ Study of PAN-90806 eye drops, suspension for neovascular AMD. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03479372. Accessed June 14, 2024.